SCTP was primarily developed for the signalling over IP networks i.e. SIGTRAN. But these days many more applications are finding SCTP suitable as a transport layer as compare to TCP. In this article I am trying to compare the SCTP with TCP.
1) TCP supports single stream of data delivery where as SCTP supports multi-streams of data delivery. Because of single stream behavior TCP has head of the line blocking issue i.e. a packet has to wait for the delivery of previous packet even though it is not the related packet. But in SCTP they can follow different stream and avoid the head of the line blocking.
2) SCTP supports MultiHoming which means single SCTP endpoint to have multiple IP addresses. The main reason for this is to maintain the availability of the endpoint via several redundant routing paths and application is available even though one path is failed.
3) Traditional TCP uses a three-way handshake, whereas SCTP uses a four-way handshake. A signed state cookie is involved in the SCTP four-way handshake, which helps to protect from denial of service attacks. Or in short we can say SCTP is more secure.
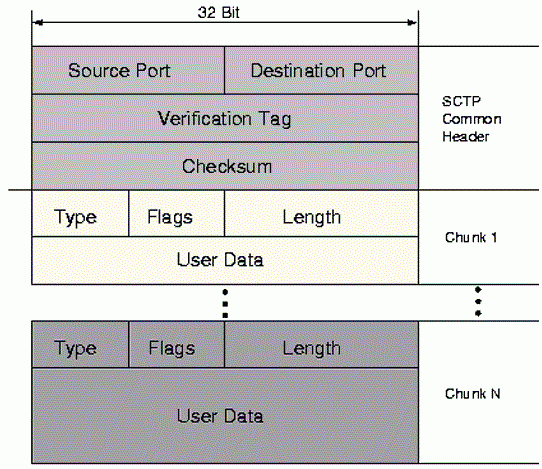
4) SCTP packets are called chunks and allows chunk bundling and segmentation whereas TCP is stream and does not preserve the message boundary.
5) SCTP is more flexible as compare to TCP is allows multi streaming or single streaming, ordered or unordered delivery, bundling or non bundling.
6) In the similar environment SCTP provides the better performance as compare to TCP.
7) SCTP is defined in RFC4960 where as TCP in RFC 793
8) Having so many advantage TCP is more widely used and more wrapper or plugins are available for the TCP.
SCTP Header
TCP Header

